A fully detailed explanation of your eye health status, a written diagnosis and care plan, and a sight correction prescription is provided to every patient of the Eye Clinic following your consultation.
We also provide lifestyle choice information to enable you to maximise your eye health. And we advise you on the best sight correction options for the best possible eyesight and vision comfort. On this page we provide some basic information about the types of conditions we encounter regularly.
Self-Management of any eye condition is advisable only following professional advice. Accurate information and an accurate diagnosis is essential. Generally General Practitioners and Pharmacists can only give limited advice unless your eyes are fully examined and a definitive written diagnosis has been made by an eyecare professional.
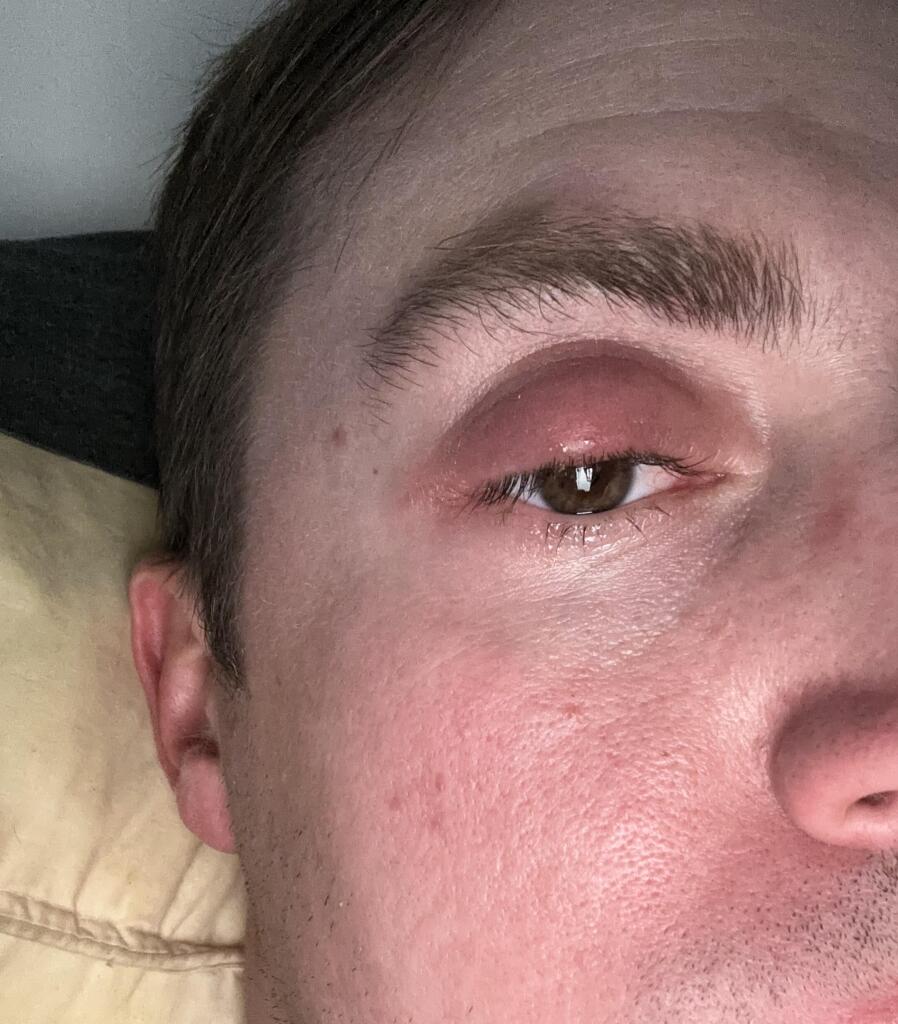
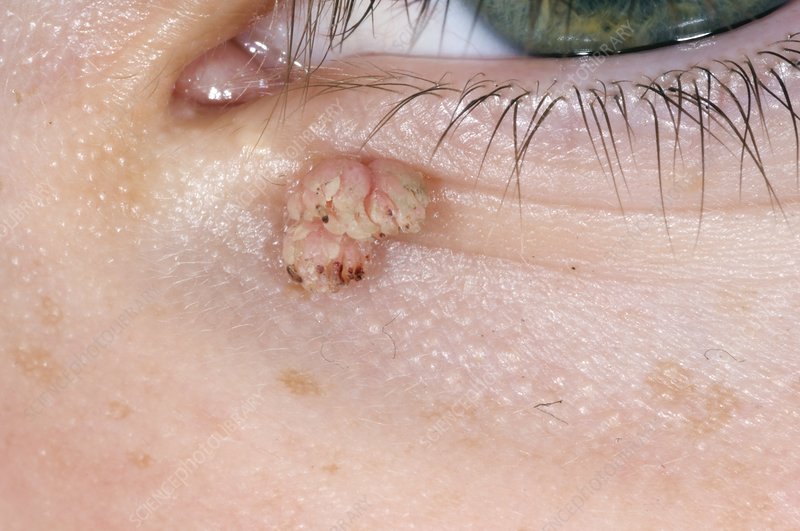
Understanding Eyelid Lumps: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment.
Eyelid lumps are common occurrences that can range from benign to potentially serious conditions. These lumps can appear on the upper or lower eyelids and may vary in size, shape, and texture. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for eyelid lumps is essential for maintaining eye health and addressing any concerns.
Causes of Eyelid Lumps
Eyelid lumps can arise from various factors, with some of the most common causes including:
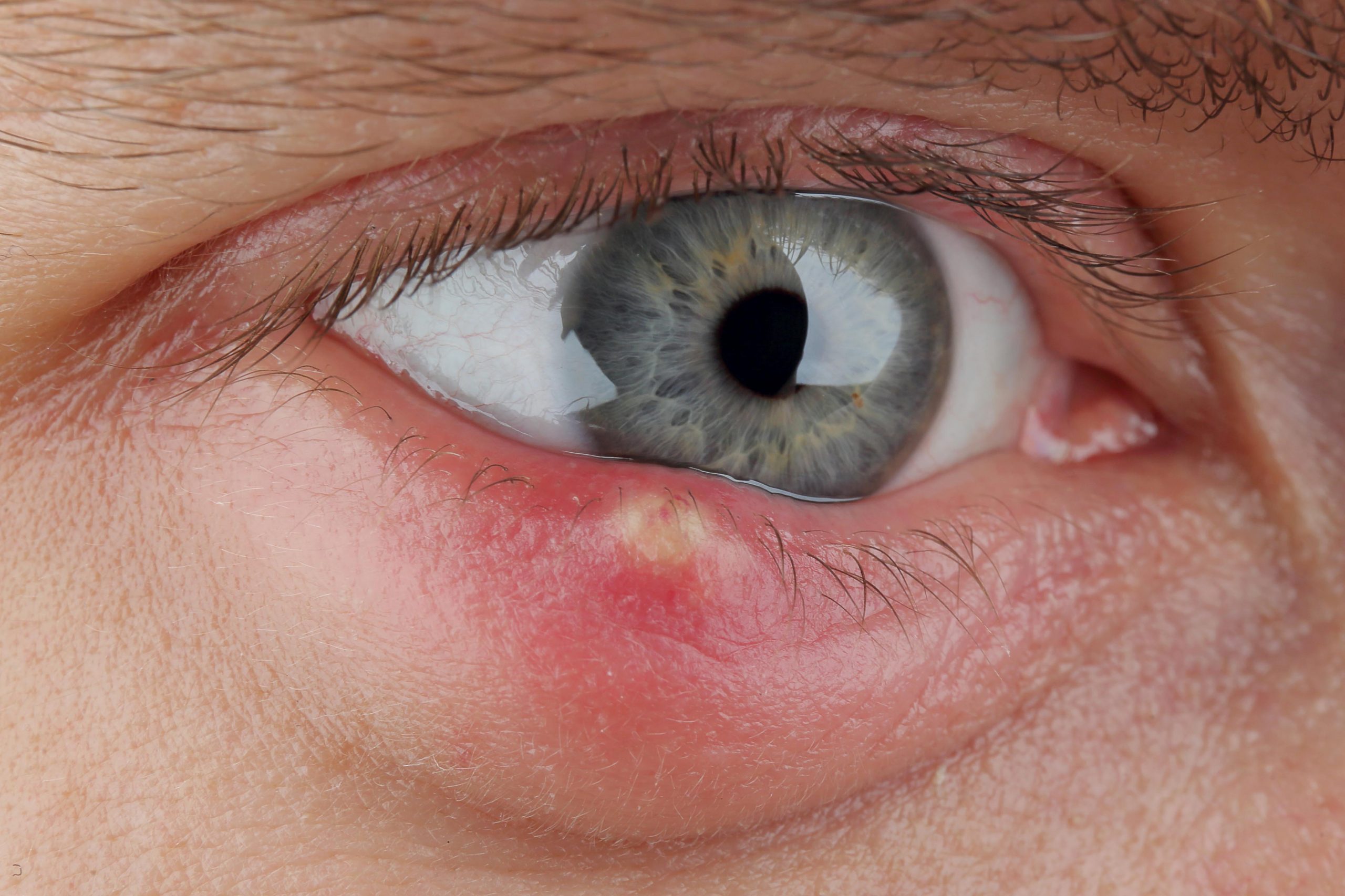
- Chalazion: A chalazion is a blockage of the oil glands in the eyelid, leading to localised swelling. It often starts as a small, painless bump but can grow larger and become uncomfortable if left untreated.
- Stye (Hordelium): A stye is an infection of the oil glands or hair follicles on the eyelid, usually caused by bacteria. It typically presents as a red, tender lump that can be painful and may produce pus.
- Cysts: Various types of cysts, such as epidermoid or sebaceous cysts, can form on the eyelids. These are generally benign and filled with fluid or semi-solid material. They may not cause any symptoms unless they become inflamed or infected.
- Dermatochalasis: This condition involves the sagging of skin on the eyelids, which can create a lump-like appearance. It is often related to ageing and may accompany other eyelid issues.
- Tumors: While rare, eyelid lumps can sometimes indicate the presence of benign or malignant tumors. Basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma are types of skin cancer that can develop on the eyelid, necessitating prompt evaluation and treatment.
- Allergic Reactions: Allergies to cosmetics, medications, or environmental factors can lead to swelling and the formation of lumps on the eyelids. This swelling is often accompanied by redness and itching.
Symptoms Associated with Eyelid Lumps
The symptoms of eyelid lumps can vary depending on the underlying cause. Common symptoms may include:
- Redness and Swelling: Affected areas may appear red and swollen, especially with infections like styes.
- Pain or Tenderness: Lumps caused by infections or inflammation can be painful to the touch.
- Discharge: In some cases, such as with styes, there may be pus or other discharge.
- Bleeding: The lump may be ulcerated or have a scab that can become dislodged causing bleeding.
- Itching or Irritation: Allergic reactions can result in itching and discomfort around the lump.
- Vision Changes: If a lump is large enough to obstruct vision, it may cause temporary visual disturbances.
Diagnosis and Treatment
If you notice a lump on your eyelid, it is essential to consult us for a proper diagnosis. We will conduct a thorough examination, and in some cases, we may perform additional tests to determine the exact nature of the lump.
Treatment options depend on the underlying cause:
- Warm Compresses: For chalazia and styes, applying warm compresses several times a day can help reduce swelling and promote drainage.
- Medications: Antibiotic ointments may be prescribed for bacterial infections. In cases of inflammation, corticosteroid injections may help reduce swelling.
- Surgical Removal: If a lump is persistent, painful, or suspected to be cancerous, surgical removal may be necessary. This is done in our treatment room under local anaesthesia.
- Observation: In the case of benign cysts or lumps that are not causing symptoms, we may recommend monitoring the condition rather than immediate intervention.
Conclusion
Eyelid lumps are a common concern, and while many are benign, it is crucial to seek attention if you notice any unusual changes especially if there is a scab, colour change, or bleeding. Understanding the causes and available treatment options can help alleviate concerns and ensure proper care. Regular eye examinations and awareness of changes in eyelid appearance can contribute to maintaining optimal eye health.
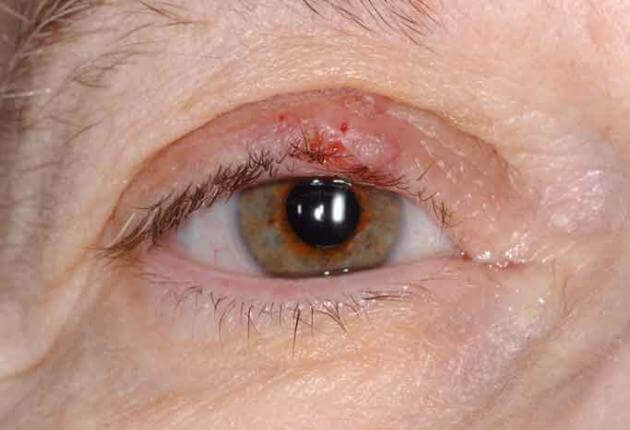
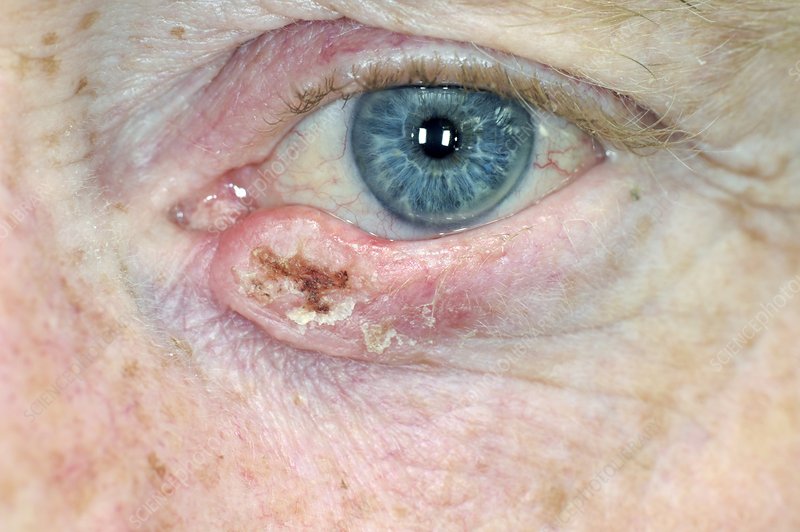
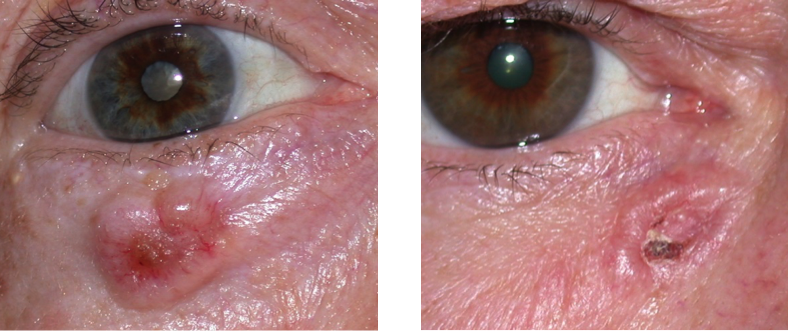


The Importance of Regular Screening for Glaucoma.
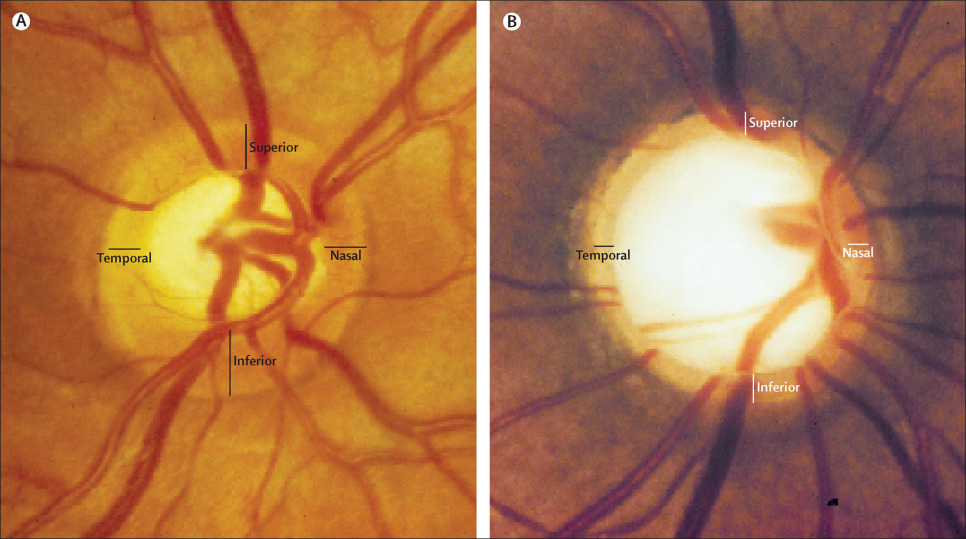
Glaucoma is often referred to as the “silent thief of sight” due to its insidious nature and the gradual loss of vision it can cause without noticeable symptoms. Typically patients will have lost 80% of their vision before they notice anything. This group of eye conditions, primarily characterised by increased intraocular pressure (IOP), can lead to irreversible damage to the optic nerve. Regular screening for glaucoma is crucial for early detection and prevention of vision loss, especially for individuals at higher risk.
Understanding Glaucoma
Glaucoma encompasses various types, with primary open-angle glaucoma being the most common. It typically develops slowly and painlessly, often going unnoticed until significant vision loss has occurred. This makes regular eye examinations essential, as many individuals are unaware they have the condition until it is too late. The risk factors include age, family history, ethnicity, and other medical conditions such as diabetes or hypertension.
The Importance of Early Detection
The primary reason regular screening is vital is that early detection can significantly change the course of the disease. When glaucoma is identified in its early stages, there are various treatment options available that can help manage the condition and preserve vision. These treatments may include prescription eye drops, laser therapy, or surgical procedures designed to lower intraocular pressure. However, once vision has been lost due to glaucoma, it cannot be restored.
Risk factors
The primary risk factor in developing glaucoma is age. The incidence of glaucoma in the population at age 40 is 3/1000. By age 75 it is between 80 and 120/1000. If you have a parent with glaucoma your risk is trebled. If you have a sibling with glaucoma the risk increases to five times the normal risk. Recent studies have shown that patients who suffer from untreated obstructive sleep apnea have ten times the normal risk. There are other risk factors related to ethnic origin, eye colour, eyeball size, diabetes, short sightedness, and the use of certain medications.
Recommended Screening Guidelines
We recommend that individuals at higher risk for glaucoma begin comprehensive annual eye exams at age 30. For those with no risk factors, screening should start at age 40 and be repeated at least every two years. Patients over 60 should have annual eye examinations. Even if you do not fit into these categories, routine eye exams should be part of your healthcare regimen, as many eye conditions can be detected during these visits. Whilst you may feel your eyesight is fine, our focus is primarily to ensure your eyes are healthy.
During an examination, we perform a number of tests, including measuring intraocular pressure, the thickness of the cornea (the clear window at the front of your eye), assessing the optic nerve using 3D scanning technology, and conducting visual field tests. These assessments provide a comprehensive view of eye health and help in diagnosing glaucoma or other potential issues.
The Role of Education and Awareness
Raising awareness about glaucoma is crucial in encouraging people to seek regular screenings. Many individuals may not recognise the importance of eye health or may believe that vision changes are a normal part of ageing or feel that they can see fine so their eyes must be fine.
Or they may suffer from an irrational fear of discovering during examination that they need sight correction to make their eyesight even better, and admitting that fact to themselves represents some form of defeat and anxiety about ageing. Educational campaigns can help inform the public about the risks of glaucoma, the importance of routine eye examinations, and the potential for preserving vision through early detection.
Conclusion
Regular screening for glaucoma is an essential component of maintaining eye health, especially for those at increased risk. The disease’s asymptomatic nature makes it imperative to stay vigilant and proactive about eye care. By prioritising regular eye exams, individuals can take charge of their vision health, ensuring that any potential issues are caught early and managed effectively. In doing so, we can combat the silent threat of glaucoma and help preserve sight for future generations.
Understanding vision disturbance: causes, symptoms, and when to seek help.
Vision disturbances are changes in the way a person perceives visual information, and they can manifest in various forms, including blurriness, double vision, or even temporary loss of vision. These disturbances can be alarming and may indicate underlying health issues, making it essential to understand their causes, symptoms, and the appropriate actions to take.
Types of Vision Disturbances
Vision disturbances can occur in several forms, including:
- Blurred Vision: This is one of the most common disturbances and can affect one or both eyes. Blurriness can be caused by refractive errors like nearsightedness, farsightedness, or astigmatism, which can often be corrected with glasses or contact lenses.
- Double Vision (Diplopia): This condition occurs when a person sees two images of a single object. Diplopia can result from issues with the eye muscles, nerves, or various medical conditions affecting the brain.
- Floaters and Flashing Lights: Many people experience floaters—tiny specks or strands that drift across the field of vision. Flashing lights can appear as brief bursts of light and may indicate changes in the vitreous gel of the eye. While often harmless, they can sometimes signal more serious conditions like retinal breaks or tears which if left for even a relatively short period can lead to retinal detachment.
- Temporary Vision Loss: Sudden, temporary loss of vision in one eye can occur due to various reasons, including migraines, retinal artery occlusion, or transient ischemic attacks (TIAs).
- Visual Field Loss: This refers to a loss of peripheral vision or specific areas of the visual field. It can be caused by glaucoma, stroke, or other neurological conditions.
Causes of Vision Disturbances
The causes of vision disturbances are varied and can include:
- Refractive Errors: As mentioned, conditions like myopia, hyperopia, and astigmatism are common causes of blurred vision.
- Eye Diseases: Conditions such as cataracts, macular degeneration, diabetic retinopathy, and glaucoma can significantly affect vision.
- Neurological Conditions: Disorders affecting the brain, such as multiple sclerosis, stroke, or tumours, can lead to vision changes.
- Infections and Inflammation: Eye infections (like conjunctivitis) and inflammatory conditions (such as uveitis) can cause discomfort and visual disturbances.
- Systemic Conditions: Conditions like diabetes, hypertension, and autoimmune diseases can impact vision and overall eye health.
- Medications: Some medications may have side effects that affect vision, including blurry vision or changes in colour perception.
Symptoms Accompanying Vision Disturbances
Vision disturbances may be accompanied by other symptoms, including:
- Eye pain or discomfort
- Headaches
- Nausea
- Light sensitivity
- Difficulty focusing
When to Seek Help
While occasional vision disturbances may not be cause for serious alarm, it’s crucial to seek immediate attention if you experience:
- Sudden onset of blurred or double vision.
- Loss of vision in one or both eyes.
- Persistent floaters or flashing lights.
- Any new or unusual visual symptoms, especially if accompanied by other neurological symptoms like weakness or difficulty speaking.
Conclusion
Vision disturbances can stem from a variety of causes, ranging from benign refractive errors to serious medical conditions. Understanding the types of disturbances and their potential implications is vital for maintaining eye health. Regular eye examinations are essential for early detection and management of vision issues. If you experience any significant changes in your vision, consulting us promptly can help ensure proper diagnosis and treatment, safeguarding your sight and overall well-being.




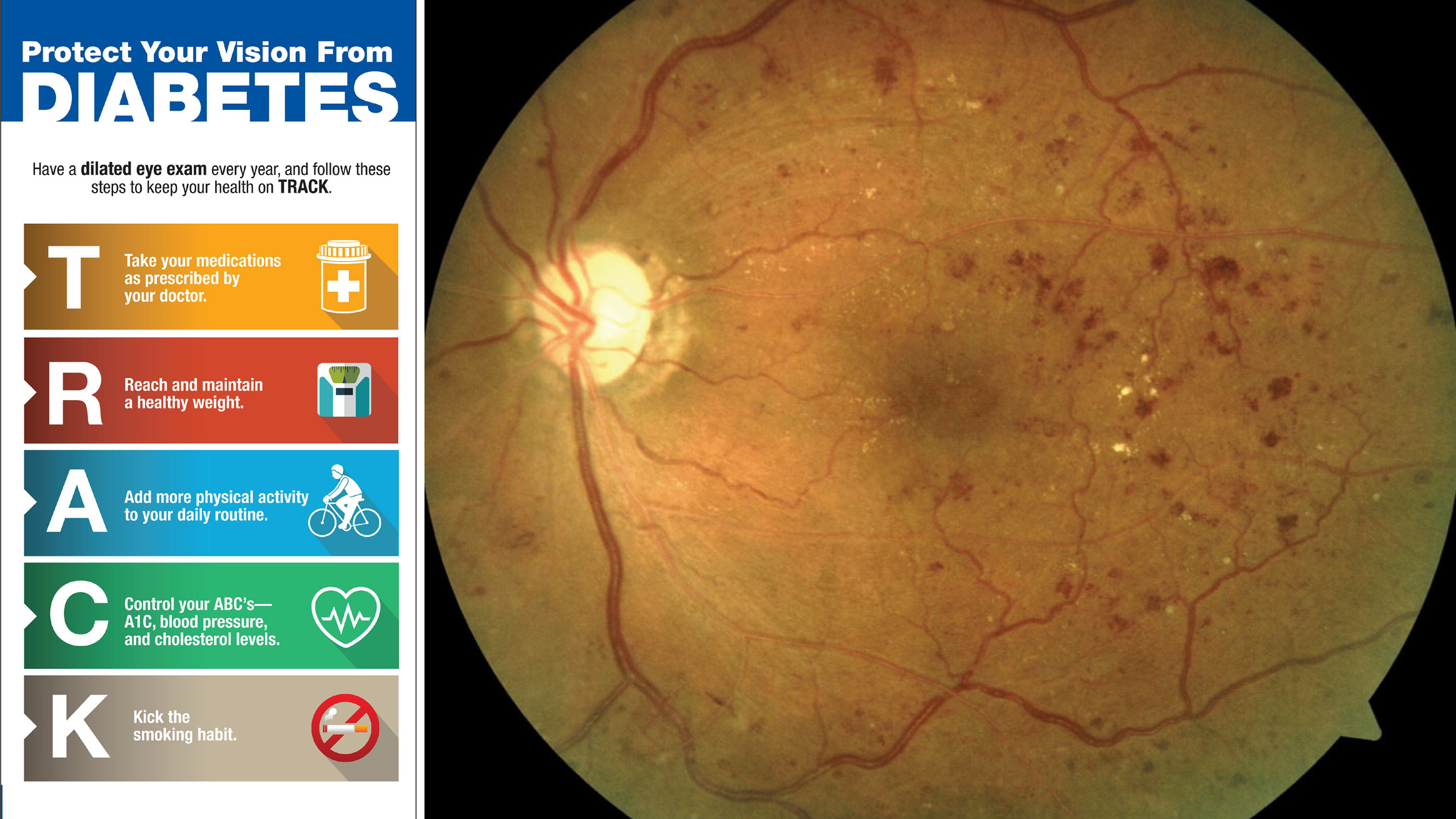
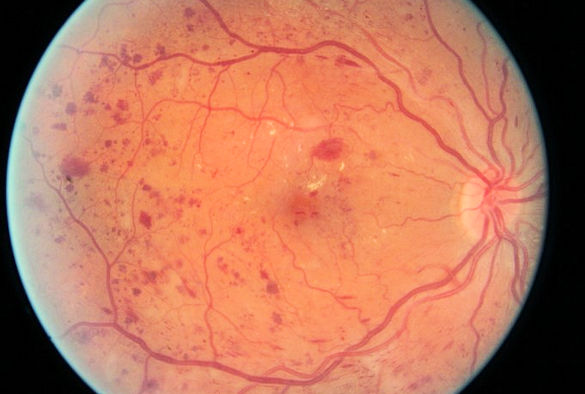
The Importance of Regular Screening for Diabetic Eye Disease.
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide, and one of its most concerning complications is diabetic eye disease. This term encompasses a range of eye problems associated with diabetes, including diabetic retinopathy, cataracts, and glaucoma. Regular screening for diabetic eye disease is crucial for early detection and timely intervention, which can prevent significant vision loss and enhance the quality of life for those living with diabetes.
Understanding Diabetic Eye Disease
Diabetic retinopathy is the most common form of diabetic eye disease, resulting from damage to the blood vessels in the retina due to prolonged high blood sugar levels. As the disease progresses, it can lead to vision impairment and even blindness. Several thousand diabetic patients in the UK are registered blind every year. Other complications such as cataracts and glaucoma can also develop more frequently and at an earlier age in individuals with diabetes. Given the potential severity of these conditions, understanding and monitoring eye health is essential for anyone diagnosed with diabetes.
The Importance of Early Detection
The primary reason regular screening is vital is that diabetic eye disease often progresses without noticeable symptoms in its early stages. Many individuals may not be aware that their vision is being compromised until significant damage has occurred. Routine eye examinations allow for the early detection of changes in the retina and other eye structures, which can be critical for effective management. Early intervention can involve adjustments in diabetes management, laser treatments, or other medical therapies that can help preserve vision.
Recommended Screening Guidelines
NICE recommends that individuals with diabetes have a comprehensive eye examination within a year of diagnosis. After the initial examination, individuals should have comprehensive eye examinations at least annually, depending on their level of risk and the presence of any eye disease. These guidelines underscore the importance of proactive care and the necessity of monitoring changes over time.
During a comprehensive eye examination, we will perform a thorough evaluation, which may include visual acuity tests, dilated fundoscopy, visual field evaluation, intraocular pressure measurement and imaging tests such as optical coherence tomography (OCT). These assessments provide vital information about the health of the retina and help identify any early signs of diabetic eye disease.
The photographic hospital based diabetic retinopathy screening service provided by HCS is not a comprehensive eye examination and it does not screen for all forms of diabetic eye disease. Patients enrolled on that service are advised by letter following the screening that they should continue to have annual eye examinations with an Optometrist.
The Role of Lifestyle Management
In addition to regular screenings, effective diabetes management plays a significant role in preventing diabetic eye disease. Maintaining blood sugar levels within target ranges, controlling blood pressure, and managing cholesterol can significantly reduce the risk of developing eye complications. Patients are encouraged to work closely with their healthcare team to develop a comprehensive plan that includes dietary changes, physical activity, and medication adherence.
Continuous glucose monitoring via an implant in the patient’s arm can revolutionise their diabetic control, by giving them real time information and helping them to avoid spikes and become more aware of and in control of the effect of their lifestyle choices. We can provide more information about this option.
Conclusion
Regular screening for diabetic eye disease is an essential part of managing diabetes and protecting vision. As diabetic eye conditions can develop silently, routine eye examinations are crucial for early detection and intervention. By prioritising eye health and adhering to screening guidelines, individuals with diabetes can take proactive steps to safeguard their vision and overall well-being. Education and awareness about the risks of diabetic eye disease and the importance of regular eye exams can empower patients to make informed decisions about their health, ultimately leading to better outcomes and a higher quality of life.
The Importance of Regular Screening for Cataracts.
Cataracts are one of the leading causes of vision impairment and blindness worldwide, particularly among older adults. A cataract occurs when the lens of the eye becomes cloudy, leading to blurred vision, difficulty seeing at night, and faded colors. While cataracts are a common part of the ageing process, regular screening is vital for early detection and timely intervention, which can significantly enhance quality of life.
Understanding Cataracts
Cataracts typically develop slowly over time, making them difficult to notice in their early stages. They can affect one or both eyes and are often associated with ageing, although other factors such as diabetes, prolonged exposure to UV rays, smoking, and certain medications can increase the risk. Symptoms may include blurred or cloudy vision, haloes around lights, and difficulty with glare, particularly when driving at night or on bright overcast days.
The Importance of Early Detection
Regular eye screenings are essential for the early detection of cataracts. Many individuals may not realise their vision is deteriorating until it significantly impacts their daily activities. During a comprehensive eye exam, we can assess the clarity of the lens, evaluate visual acuity, and determine the extent of any cataract formation. Early detection allows for monitoring and planning appropriate interventions, which can include lifestyle modifications, updated prescriptions for glasses, or, in more advanced cases, surgical options.
Screening Recommendations
We recommend regular eye examinations every two years, with frequency increasing from age 40 based on individual risk factors and changes in vision, and annual eye examinations from age 60. For those with a family history of cataracts or other eye conditions, more frequent screenings may be necessary. During these examinations, we use a variety of tests to evaluate eye health, including visual acuity tests, dilated retinal exams, and tonometry to measure intraocular pressure.
The Role of Lifestyle Factors
While cataracts cannot always be prevented, certain lifestyle choices can mitigate the risk of developing them or slow their progression. Maintaining a healthy diet rich in antioxidants, such as vitamins C and E, and omega-3 fatty acids can support eye health. Additionally, wearing UV-blocking sunglasses, avoiding smoking, and managing chronic conditions like diabetes can significantly reduce the risk of cataracts. Regular screenings can provide an opportunity to discuss these lifestyle factors with with us, promoting a proactive approach to eye health.
The Benefits of Timely Intervention
If cataracts are diagnosed, the good news is that they are highly treatable. Cataract surgery, one of the most common and effective surgical procedures performed worldwide, involves removing the cloudy lens and replacing it with an artificial one. This procedure has a high success rate and can dramatically improve vision and quality of life. However, the decision to proceed with surgery typically depends on the availability of taxpayer funded surgery, severity of symptoms and the impact on daily activities. We can discuss the options and likely benefits of earlier intervention via a private medical route.
Conclusion
Regular screening for cataracts is essential for maintaining vision health, particularly as individuals age. Early detection allows for timely intervention, which can help preserve quality of life and independence. By prioritising routine eye exams and adopting healthy lifestyle choices, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their eye health effectively. Awareness and education about cataracts and the importance of regular screenings can empower individuals to seek the care they need before they have to curtail their activities due to increasing eyesight difficulties, ultimately leading to better vision outcomes and a brighter future.

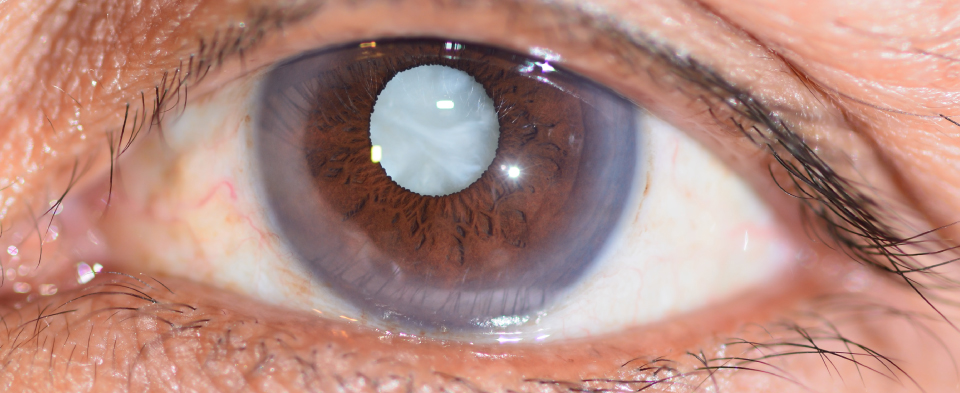
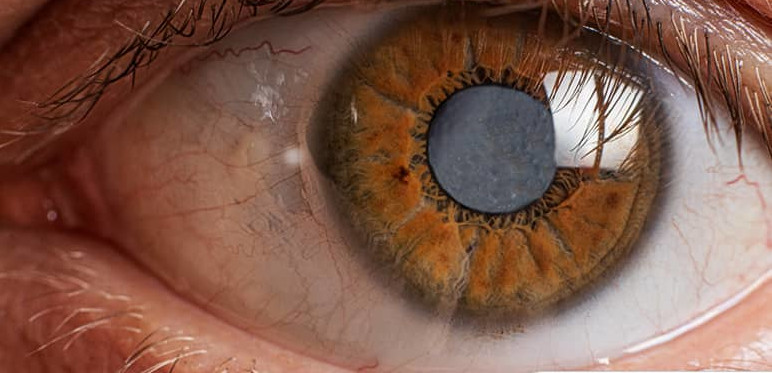
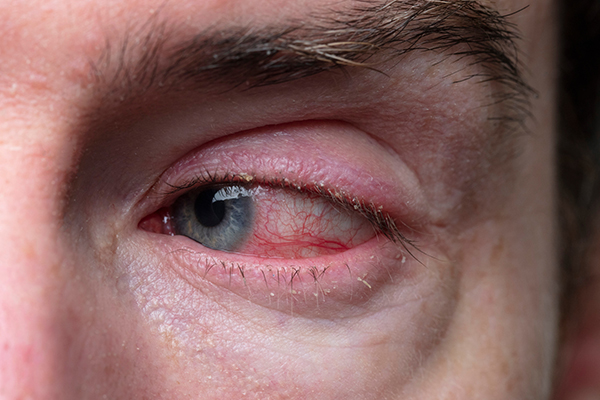
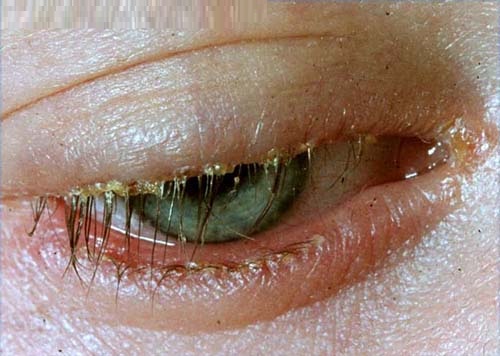
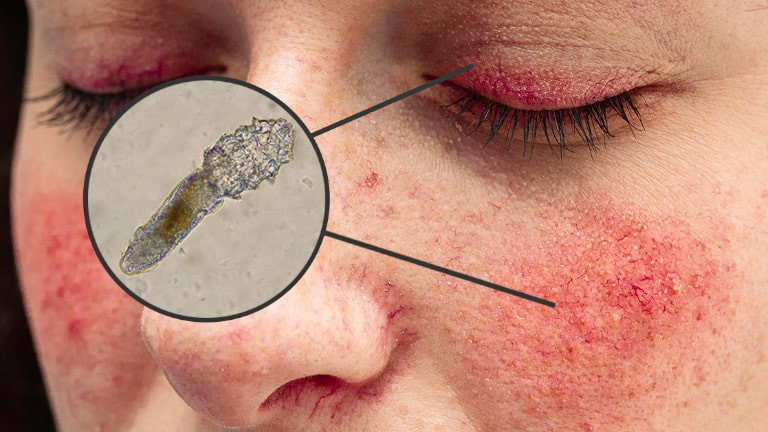
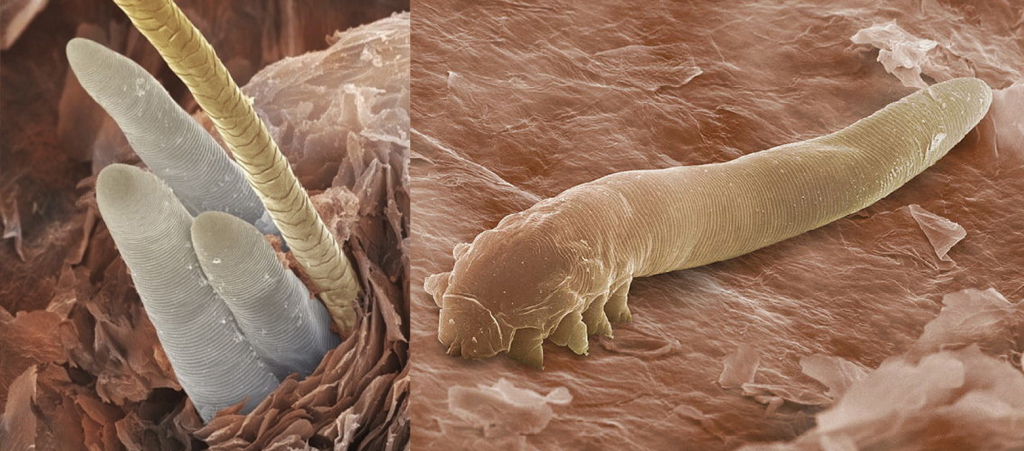
Understanding Blepharitis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment.
Blepharitis is a common and often chronic condition characterised by inflammation of the eyelid margins. It can affect individuals of all ages and may result in discomfort and visual disturbances. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for blepharitis is essential for effective management and relief.
What Causes Blepharitis?
Blepharitis can be caused by a variety of factors, and it often occurs in two primary forms: seborrheic blepharitis and staphylococcal blepharitis.
- Seborrheic Blepharitis: This type is associated with seborrheic dermatitis, a skin condition that leads to oily, flaky skin, often affecting areas like the scalp and face. It occurs when sebaceous glands produce excess oil, leading to irritation and inflammation along the eyelid margins.
- Staphylococcal Blepharitis: This form is caused by an overgrowth of staphylococcal bacteria that naturally inhabit the skin. When the balance of bacteria is disrupted, it can lead to infection and inflammation of the eyelids.
- Demodex skin mites: Demodex mites are symbiotic mites which live in the eyelash follicles. Normally they co-exist with us and feed on dead skin cells without causing any signs or symptoms. However in some individuals they cause a reaction which leads to blepharitis. Often this is accompanied by rosacea which causes cheeks to be red.
Additional factors contributing to blepharitis include allergies, dry eye syndrome, and certain skin conditions such as rosacea or eczema. Poor eyelid hygiene can also exacerbate the problem, allowing debris, dead skin cells, and bacteria to accumulate.
Symptoms of Blepharitis
The symptoms of blepharitis can vary in severity and may include:
- Redness and Swelling: The eyelid margins may appear inflamed and swollen.
- Itching and Burning: Many individuals experience itching or a burning sensation in the eyes.
- Crusty Eyelids: In the morning, crusts may form on the eyelids, making it difficult to open the eyes.
- Flaky Skin: Scaling or flaking may occur along the eyelid margins.
Tearing and Dryness: Some individuals may notice increased tearing, while others may experience dryness and discomfort.
Sensitivity to Light: Bright lights may cause discomfort or glare. You may also experience increased glare outdoors, even on overcast days
Diagnosing Blepharitis
Diagnosis typically involves a comprehensive eye examination, we assess the eyelids, inquire about symptoms, and may ask about any underlying skin conditions. In some cases, a sample may be taken to rule out other infections or conditions.
Treatment Options
While blepharitis can be challenging to manage, several treatment options can help alleviate symptoms and control inflammation:
- Good Eyelid Hygiene: Regular cleaning of the eyelid margins is crucial. Patients are given written advice on the use of warm compresses followed by eyelid scrubs to remove crusts and debris.
- Topical Medications: Antibiotic ointments or drops may be prescribed to address bacterial overgrowth, particularly in cases of staphylococcal blepharitis. Steroid eye drops or ointments may be used to reduce inflammation.
- Artificial Tears: For individuals experiencing dry eyes, preservative-free artificial tears can provide relief and help maintain moisture.
- Management of Underlying Conditions: If blepharitis is associated with skin conditions like rosacea or seborrheic dermatitis, treating these underlying issues can improve symptoms.
- Regular Follow-Up: Chronic cases may require ongoing proactive rather than reactive management, including regular follow-up appointments to monitor symptoms and adjust treatment as necessary.
Conclusion
Blepharitis, while common, can significantly impact quality of life due to discomfort and visual disturbances. Understanding its causes, recognising symptoms, and adhering to proactive treatment plans are crucial for effective management. With proper care and attention, individuals can find relief from blepharitis and maintain healthy eyelids and vision. If you suspect you have blepharitis, consult us for a thorough evaluation and personalised treatment plan.
Understanding Sore Eyes: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment.
Sore eyes, often described as a feeling of discomfort, pain, or irritation in the eyes, can significantly impact daily activities and quality of life. This common issue can arise from a variety of sources, including environmental factors, underlying health conditions, and excessive screen time. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for effective management.
What Causes Sore Eyes?
Sore eyes can result from numerous factors, including:
- Environmental Irritants: Exposure to smoke, dust, pollen, and strong odours can lead to irritation and discomfort in the eyes. These irritants can trigger inflammation, causing the eyes to feel sore or scratchy.
- Allergies: Allergic reactions to substances like pollen, pet dander, or mould can cause sore eyes. Symptoms often include redness, itching, and tearing, which can exacerbate the feeling of soreness.
- Dry Eye Syndrome: Insufficient tear production or excessive tear evaporation can lead to dry eyes and hypersalinity of the tears, resulting in a sore, gritty sensation. This condition is often exacerbated by prolonged screen time, air conditioning, and certain medications.
- Infections: Viral or bacterial infections, such as conjunctivitis (pink eye), can cause sore eyes. In addition to pain, symptoms may include redness, discharge, and swelling.
- Eye Strain: Extended periods of reading, computer use, or focusing on tasks can lead to eye strain, resulting in soreness and discomfort. This is particularly common in our digital age, where screens dominate our daily activities.
- Injuries: Trauma to the eye, whether from a foreign object, chemical exposure, or accidental scratches, can cause immediate soreness and discomfort.
- Systemic Conditions: Health issues such as rheumatoid arthritis, thyroid problems, or autoimmune diseases can also contribute to sore eyes by affecting tear production or causing inflammation.
- Contact Lens Wear: Improper use of contact lenses, such as wearing them for too long or not cleaning them adequately, or using legacy material lenses because they are cheaper, can lead to irritation and soreness.
Symptoms Associated with Sore Eyes
In addition to the primary symptom of soreness, individuals may experience other related symptoms:
- Redness: The eyes may appear red or bloodshot, indicating irritation or inflammation.
- Itching or Burning: Many people with sore eyes report accompanying sensations of itching or burning.
- Tearing: Increased tearing can occur as the eyes attempt to flush out irritants.
- Sensitivity to Light: Bright lights may cause discomfort, leading to squinting or avoidance of light sources.
- Blurred Vision: Temporary visual disturbances can accompany soreness, especially if caused by eye strain or fatigue.
- Inadequate Blinking: A hidden symptom due to spreadsheet use, or extensive mouse use and concentration, resulting in infrequent blinking that causes symptoms.
Diagnosing Sore Eyes
To determine the underlying cause of sore eyes, we will conduct a thorough examination. This may include a review of medical history, visual acuity tests, and assessments of tear production and eye health.
Treatment Options
The treatment for sore eyes largely depends on the underlying cause:
- For Allergies: Special eye drops or tablets can help alleviate symptoms. Avoiding known allergens is also crucial.
- For Dry Eyes: Artificial tears can provide relief. Lifestyle adjustments, such as taking breaks during screen time and using humidifiers, can also help.
- For Infections: Bacterial conjunctivitis may require antibiotic eye drops, while viral conjunctivitis typically resolves on its own with supportive care.
- For Eye Strain: Practicing the 20-20-20 rule—looking at something 20 feet away for 20 seconds every 20 minutes—can help reduce eye strain. Having the correct sight correction tailored to your work environment requirements is also essential.
- For Injuries: Seek immediate medical attention for serious injuries or chemical exposures. Minor injuries may require gentle rinsing and observation.
Conclusion
Sore eyes are a common complaint that can stem from various causes, ranging from environmental factors to underlying medical conditions. Recognising the symptoms and understanding potential triggers can aid in effective management. If sore eyes persist or are accompanied by severe symptoms, consulting us is essential for proper diagnosis and treatment, ensuring optimal eye health and comfort. Taking proactive steps to care for your eyes can help prevent discomfort and maintain clear vision.

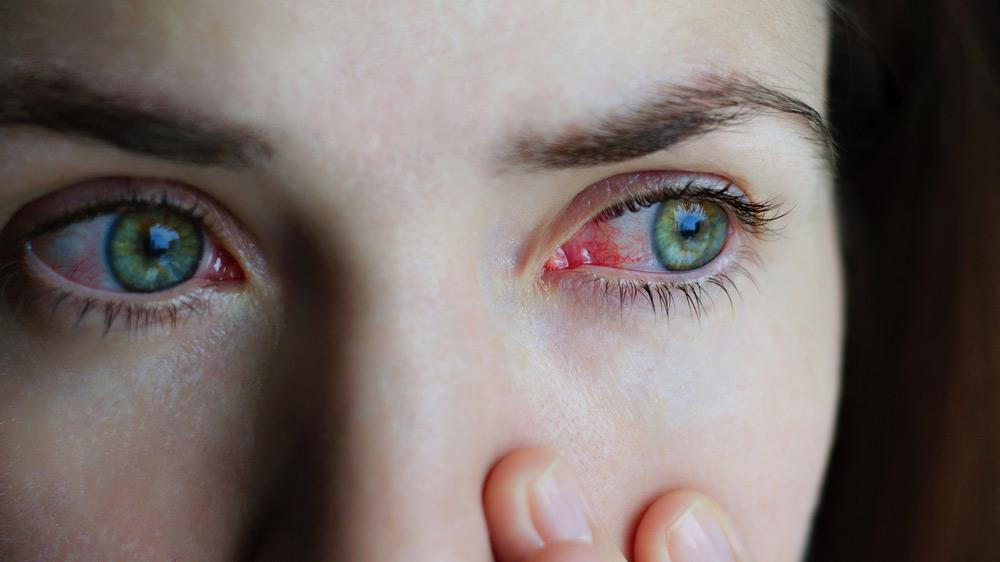

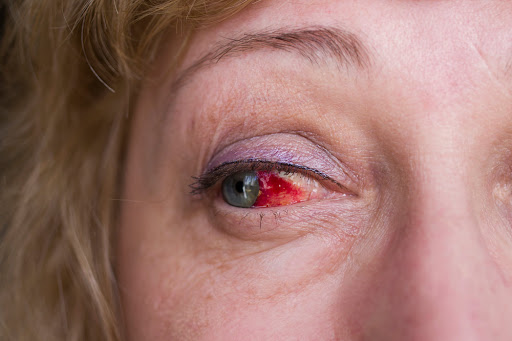
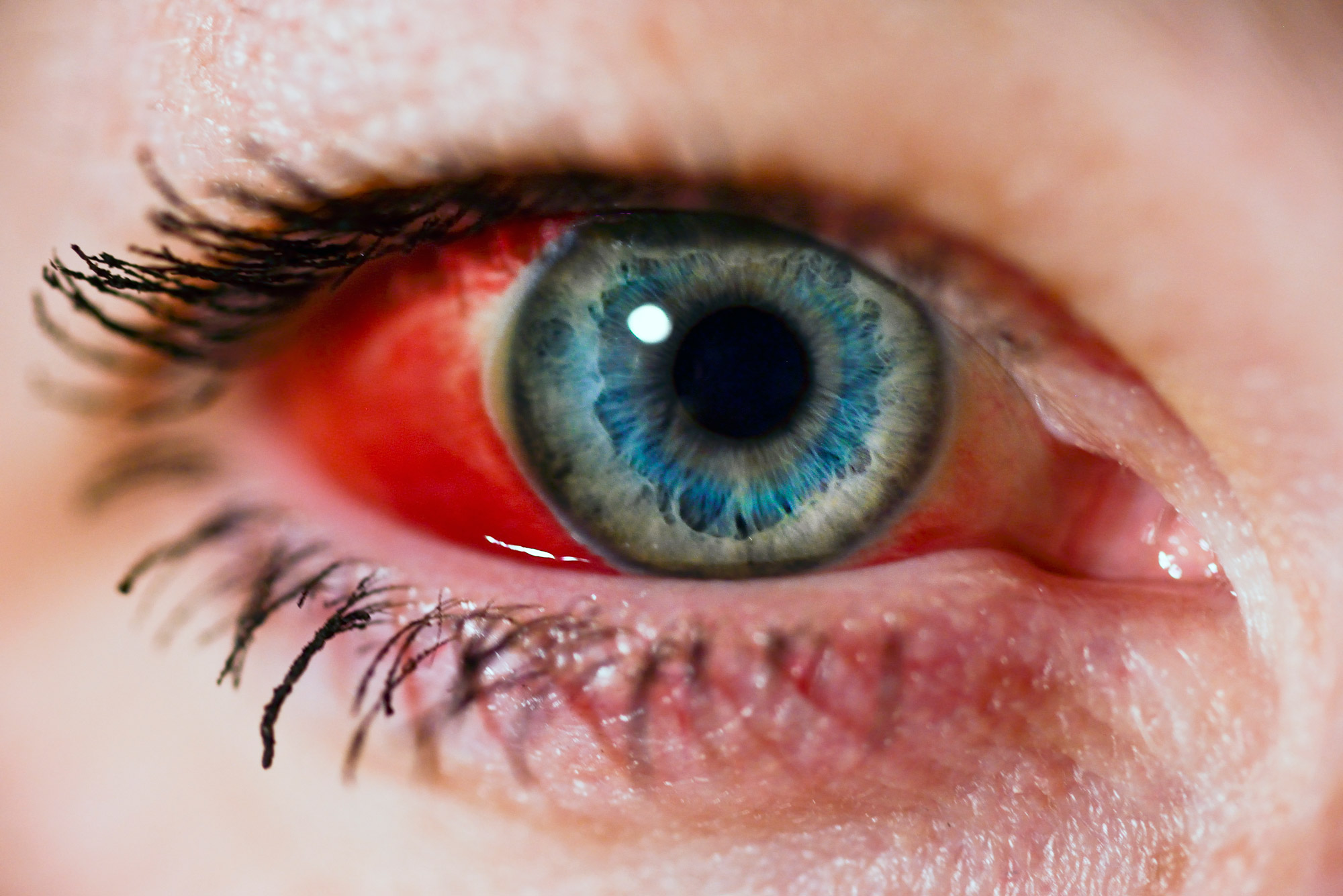
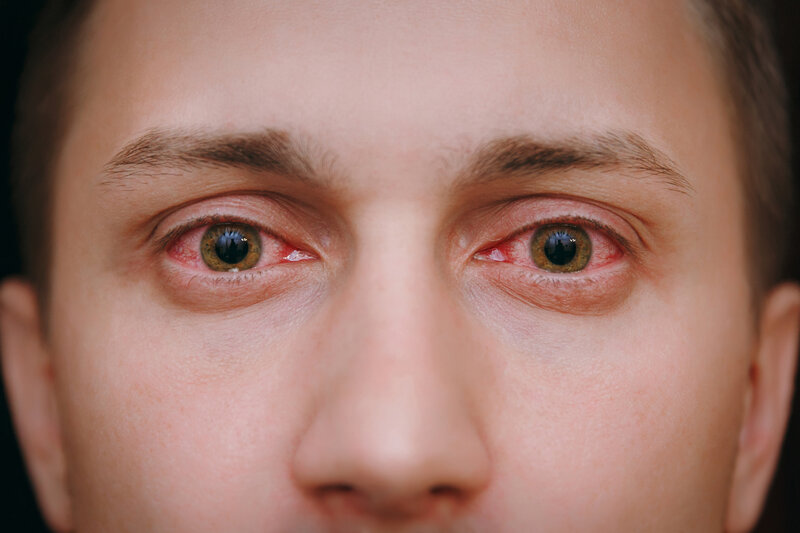
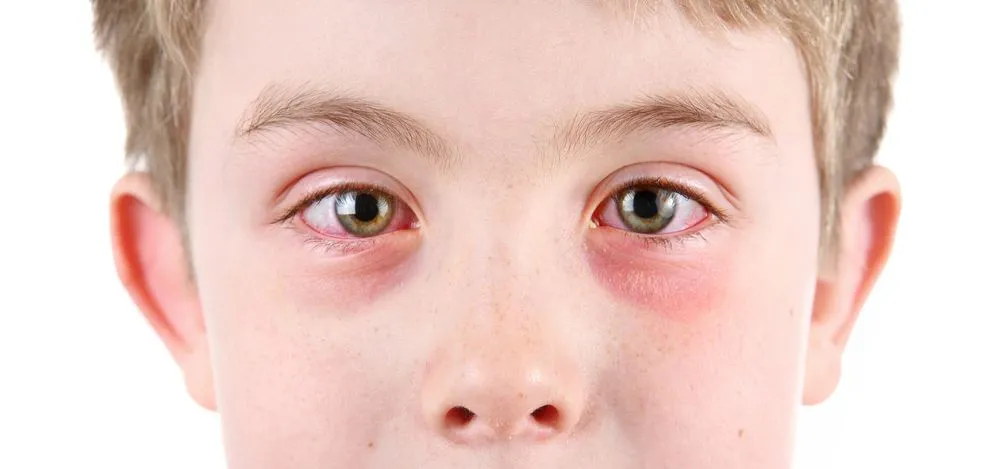
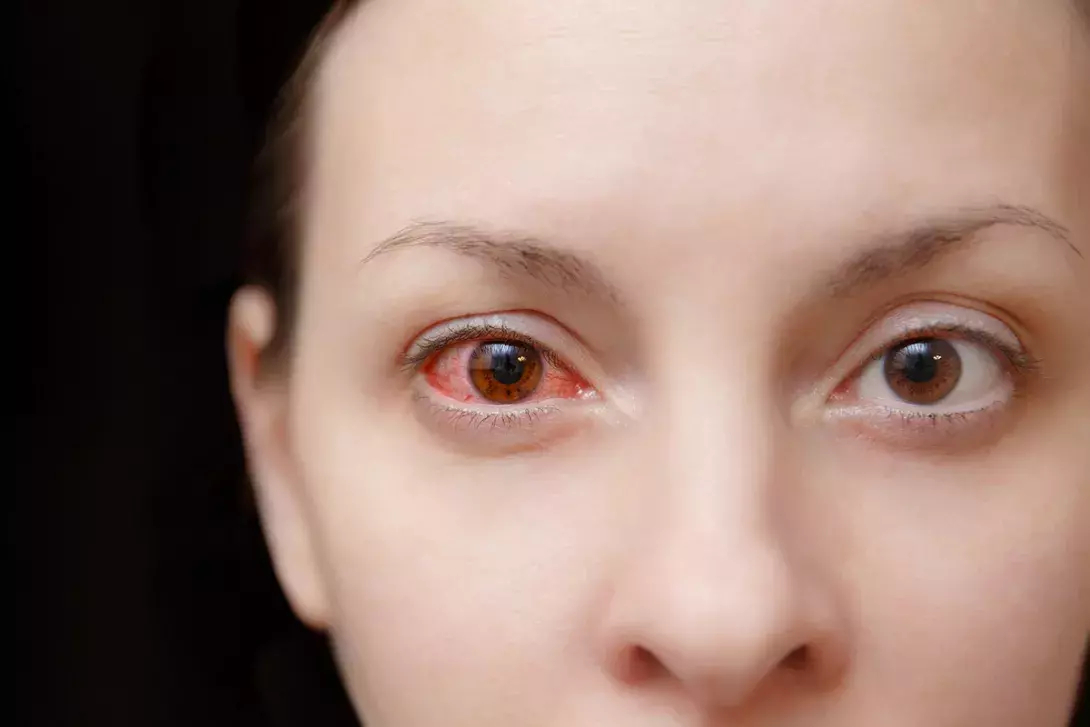
Understanding Red Eye: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment.
Red eye is a common condition characterised by the appearance of redness in the white part of the eye, known as the sclera. While it might seem like a minor issue, red eye can be a sign of various underlying problems, ranging from benign to serious. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for effective management and maintaining eye health.
What Causes Red Eye?
Red eye can result from a variety of factors, including:
- Allergies: Allergic reactions to pollen, dust, pet dander, or other allergens can cause inflammation and redness in the eyes. This is often accompanied by itching, tearing, and swelling.
- Infections: Conjunctivitis, commonly known as pink eye, is an inflammation of the conjunctiva, the thin membrane covering the eye and inner eyelids. It can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or allergens and typically leads to redness, discharge, and discomfort.
- Irritants: Smoke, pollution, chlorine from swimming pools, and other environmental irritants can cause the eyes to become red and inflamed. Prolonged exposure to these irritants can exacerbate the condition.
- Injuries: Trauma to the eye, such as scratches or foreign objects, can lead to redness and irritation. If the injury is serious, it may also cause pain and changes in vision.
- Dry Eye: Insufficient tear production or excessive evaporation can lead to dryness and irritation, resulting in redness. This is often exacerbated by environmental factors, prolonged screen time, or contact lens wear.
- Subconjunctival Haemorrhage: This occurs when a small blood vessel breaks just beneath the conjunctiva, resulting in a bright red patch on the white part of the eye. It is often harmless and resolves on its own, but it can be alarming to see.
- Glaucoma: Acute glaucoma, a condition characterised by increased pressure in the eye, can cause severe redness, pain, and vision changes. This is a medical emergency and requires immediate attention.
- Systemic Conditions: Certain systemic diseases, such as hypertension or autoimmune disorders, can also contribute to red eye by affecting blood vessels in the eyes.
Symptoms of Red Eye
The primary symptom of red eye is the noticeable redness of the sclera. However, associated symptoms can vary depending on the underlying cause and may include:
- Itching or Burning: Often due to allergies or dryness.
- Discharge: Watery or thick discharge can indicate an infection.
- Swelling: Puffiness around the eyes may accompany redness, particularly in allergic reactions.
- Vision Changes: Blurred vision or haloes around lights can occur with more serious conditions like glaucoma.
Diagnosing Red Eye
To diagnose the cause of red eye, we will conduct a comprehensive eye examination, which may include a review of medical history, visual acuity tests, and evaluation of eye structures using specialised instruments.
Treatment Options
Treatment for red eye depends on the underlying cause:
- Allergic Reactions: Antihistamine eye drops or oral antihistamines can alleviate symptoms.
- Infections: Bacterial conjunctivitis may require antibiotic eye drops, while viral conjunctivitis typically resolves on its own.
- Irritants: Rinsing the eyes with saline solution and avoiding irritants can help reduce symptoms.
- Dry Eye: Artificial tears and lifestyle changes, such as taking breaks from screens, can improve symptoms.
- Injury: Treatment will vary depending on the severity of the injury and may require medical intervention.
- Glaucoma: This requires immediate medical attention and treatment to lower intraocular pressure.
Conclusion
Red eye is a common symptom that can arise from various causes, ranging from mild irritations to serious conditions. Awareness of the potential underlying issues and associated symptoms is crucial for effective management. If you experience persistent or severe red eye symptoms, it is important to consult us for a thorough evaluation and appropriate treatment. Taking care of your eye health can help prevent complications and maintain clear vision.
Understanding Dry Eye: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment.
Dry eye is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide, characterised by insufficient lubrication on the surface of the eye. This can lead to discomfort, visual disturbances, and even damage to the eye’s surface if left untreated. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for dry eye is essential for managing this condition effectively.
What Causes Dry Eye?
Dry eye occurs when the eyes do not produce enough tears or when the tears evaporate too quickly. Several factors can contribute to this condition:
- Ageing: As people age, tear production can decrease, making dry eye more common in older adults.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to wind, smoke, dry climates, and air conditioning can increase tear evaporation, leading to dryness.
- Medical Conditions: Certain health conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes, and thyroid disorders, can affect tear production. Additionally, autoimmune diseases like Sjögren’s syndrome specifically target moisture-producing glands, leading to dry eye symptoms.
- Medications: Some medications, including antihistamines, antidepressants, and blood pressure medications, can reduce tear production as a side effect.
- Screen Time: Increased use of digital devices can contribute to dry eye, as people tend to blink less frequently when focusing on screens.
- Contact Lenses: Wearing contact lenses can exacerbate dry eye symptoms, as lenses can interfere with the natural tear film.
Symptoms of Dry Eye
The symptoms of dry eye can vary in severity and may include:
- Burning or Stinging Sensation: Many individuals report a feeling of dryness or irritation in the eyes.
- Redness: The eyes may appear red or inflamed.
- Sensitivity to Light: Bright lights can cause discomfort or glare.
- Blurred Vision: Visual disturbances may occur, often improving with blinking but returning with extended screen time or focus.
- Excessive Tearing: Paradoxically, dry eye can lead to excessive tearing as the eyes attempt to compensate for dryness.
Diagnosing Dry Eye
Diagnosis of dry eye typically involves a comprehensive eye examination by an eye care professional. The doctor will assess symptoms, review medical history, and perform tests to measure tear production and evaluate the quality of tears. Common tests include the Schirmer test, which measures tear production, and the tear break-up time test, which assesses the stability of the tear film. Dyes are also added to the tear film which stain dried out cells on the ocular surface.
Treatment Options
While dry eye can be a chronic condition, several treatment options can help alleviate symptoms:
- Artificial Tears: Over-the-counter artificial tears are often the first line of treatment. These lubricating eye drops can provide immediate relief from dryness.
- Prescription Medications: In more severe cases, prescription medications may be recommended to reduce inflammation and increase tear production.
- Punctal Plugs: These tiny devices can be inserted into the tear ducts to block drainage, helping to retain tears on the surface of the eye.
- Lifestyle Changes: Simple modifications, such as taking regular breaks from screens, using a humidifier, and staying hydrated, can help manage symptoms.
- Warm Compresses: Applying warm compresses to the eyes can help unclog oil glands in the eyelids, improving the quality of the tear film and reducing evaporation of the tears.
- Dietary Supplements: Omega-3, 6 and 9 fatty acids have been shown to improve tear production and may be beneficial for individuals with dry eye.
Conclusion
Dry eye is a prevalent condition that can significantly impact daily life. Recognising the causes and symptoms is crucial for effective management. With a combination of lifestyle adjustments, supportive treatments, and prescription options, individuals can find relief from dry eye symptoms and maintain healthy eyes. If you experience persistent dry eye symptoms, consult us for a comprehensive evaluation and personalised treatment plan.
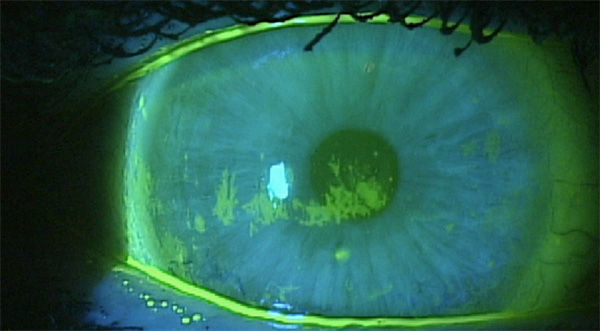
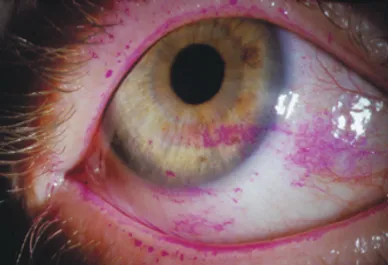

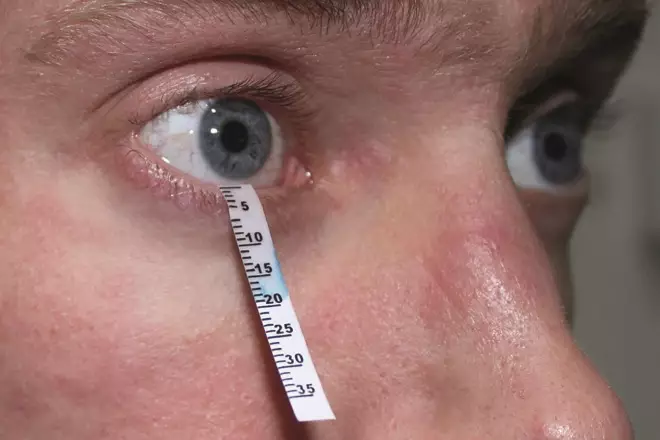
Understanding Watery Eyes: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments.
Watery eyes, also known as epiphora, is a common condition that many people experience at some point in their lives. While it may seem trivial, persistent watery eyes can be uncomfortable and may indicate underlying health issues. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatments can help individuals manage this condition effectively.
Causes of Watery Eyes
Watery eyes can arise from various factors, ranging from environmental irritants to medical conditions. Here are some common causes:
- Allergies: Allergic reactions to pollen, dust, pet dander, or certain foods can cause the eyes to produce excess tears. This response is the body’s way of flushing out allergens.
- Dry Eye Syndrome: Paradoxically, dry eyes can lead to watery eyes. When the eyes lack sufficient moisture, they may overcompensate by producing more tears. This condition is often exacerbated by prolonged screen time, environmental factors, or certain medications.
- Infections: Conjunctivitis (pink eye), a common eye infection, can cause inflammation and increased tear production. Viral and bacterial infections can lead to discharge and redness, often accompanying watery eyes.
- Blocked Tear Ducts: Tear ducts can become blocked due to various reasons, including infections, inflammation, or structural issues. When tears cannot drain properly, they accumulate and cause excessive tearing.
- Ingrowing eyelashes: Errant or ingrowing eyelashes can rub against the eye and cause a foreign body sensation that results in constant excessive tear production.
- Eyelid disorders: Entropion (turning in) or Ectropion (turning out) of the eyelid margins can interrupt normal tear function and result in particularly problematic watery eye.
- Environmental Factors: Wind, smoke, and pollutants can irritate the eyes, prompting them to produce more tears. Spending time in dry or dusty environments can also lead to watery eyes.
- Foreign Objects: If a foreign object, such as dust or sand or an eyelash, gets into the eye, it can cause irritation and excessive tearing as the body attempts to wash it away.
Symptoms Associated with Watery Eyes
In addition to excessive tearing, watery eyes may be accompanied by other symptoms, including:
- Redness or swelling of the eyes
- Itching or burning sensations
- Sensitivity to light
- Blurred vision
- Discharge from the eyes, which may be clear, yellow, or green, depending on the cause
Diagnosis and Treatment
If watery eyes persist, it is essential to consult an eye care professional for a proper diagnosis. The doctor will conduct a thorough examination and may ask about medical history and symptoms to determine the underlying cause.
Treatment options for watery eyes vary based on the cause:
- Allergy Management: Antihistamines, both oral and topical, can help alleviate symptoms related to allergies. Reducing exposure to allergens is also crucial.
- Artificial Tears: For dry eye syndrome, using artificial tears can provide relief and help balance tear production.
- Infection Treatment: Bacterial conjunctivitis may require antibiotic eye drops, while viral infections usually resolve on their own.
- Syringing of the tearducts: Dilation of the entrance to the tearducts and syringing the ducts with saline can often improve drainage and clear blockages.
- Electrolysis: Electrolysis of errant and ingrowing eyelashes is a more permanent solution than regular epilation.
- Surgery: In cases of severely blocked tear ducts, minor surgical intervention may be necessary to restore proper drainage. Eyelid surgery can also correct Ectropion and Entropion.
- Environmental Adjustments: Wearing sunglasses outdoors, using humidifiers, and taking regular breaks from screens can mitigate symptoms caused by environmental factors.
Conclusion
Watery eyes can be a nuisance, but understanding their causes and symptoms is the first step toward effective management. By identifying underlying issues and seeking appropriate treatment, individuals can alleviate discomfort and maintain their eye health. If watery eyes persist or are accompanied by severe symptoms, consulting us is essential for proper diagnosis and treatment.
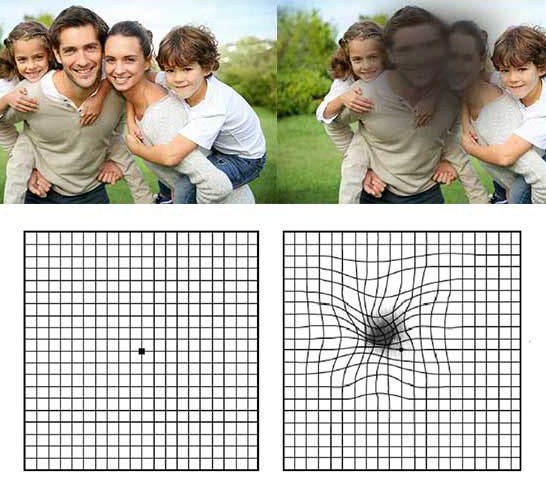
The Importance of Regular Screening for Age-Related Macular Degeneration.
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is a leading cause of vision loss among older adults, affecting millions worldwide. As we age, the risk of developing AMD increases, making regular screening essential for early detection and effective management. Understanding the importance of these screenings can empower individuals to take proactive steps in preserving their vision.
Understanding AMD
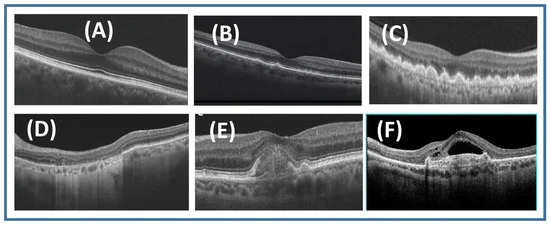
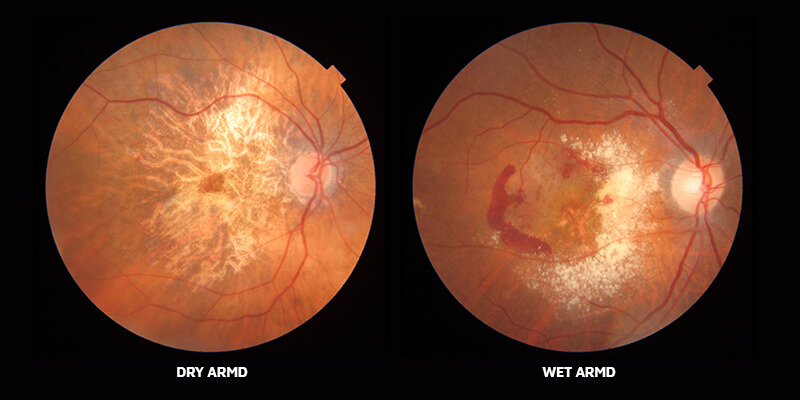
AMD primarily affects the macula, the part of the retina responsible for central vision. There are two main types: dry AMD and wet AMD. Dry AMD is more common and progresses slowly, while wet AMD can lead to rapid vision loss due to fluid leakage beneath the retina. Symptoms may include blurred or distorted vision, difficulty recognising faces, and the presence of dark spots in the central vision.
The Need for Regular Screening
- Early Detection: Regular eye exams are crucial for catching AMD in its early stages. Many individuals do not notice the subtle changes in their vision until the disease has progressed significantly. Through routine screenings, we can identify early signs of AMD, allowing for timely intervention.
- Monitoring Progression: For those already diagnosed with AMD, regular screenings help monitor the condition’s progression. This ongoing assessment enables us to adjust treatment plans as needed, potentially slowing down vision loss. Advanced imaging techniques, like optical coherence tomography (OCT), allow for detailed views of the retina, providing valuable insights into changes over time.
- Access to Treatment Options: Early detection through regular screening opens doors to various treatment options. For those with wet AMD, medications that inhibit the growth of abnormal blood vessels can be administered to prevent further vision loss. For dry AMD, lifestyle modifications and nutritional supplements may help slow progression. Regular check-ups ensure that individuals can access these treatments promptly.
- Awareness of Risk Factors: Regular screenings also serve as an opportunity for patients to discuss risk factors with us. Factors such as age, family history, smoking, and diet can influence the likelihood of developing AMD. Being aware of these risks allows individuals to make informed lifestyle choices that can potentially reduce their risk.
- Educational Opportunities: We can provide education on the importance of eye health and the role of regular screenings. Patients can learn about the symptoms of AMD, the significance of maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and the benefits of protective eyewear against harmful UV rays.
- Quality of Life: Vision is a crucial component of daily life, impacting everything from reading to driving and social interactions. By prioritising regular screenings for AMD, individuals can take control of their eye health, ultimately improving their quality of life. Early intervention can help maintain independence and enhance overall well-being.
Conclusion
In conclusion, regular screening for age-related macular degeneration is vital for preserving vision and maintaining quality of life as we age. With early detection, effective monitoring, and access to treatment options, individuals can combat the impacts of AMD. It is essential for those over the age of 60, or those with risk factors over the age of 50, to undergo annual eye examinations and stay informed about their eye health. By prioritising regular screenings, we can work towards a future where age-related vision loss is minimised, allowing individuals to continue to enjoy life with clarity and confidence.

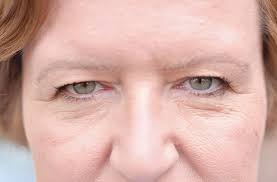
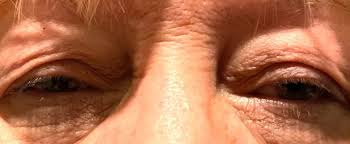
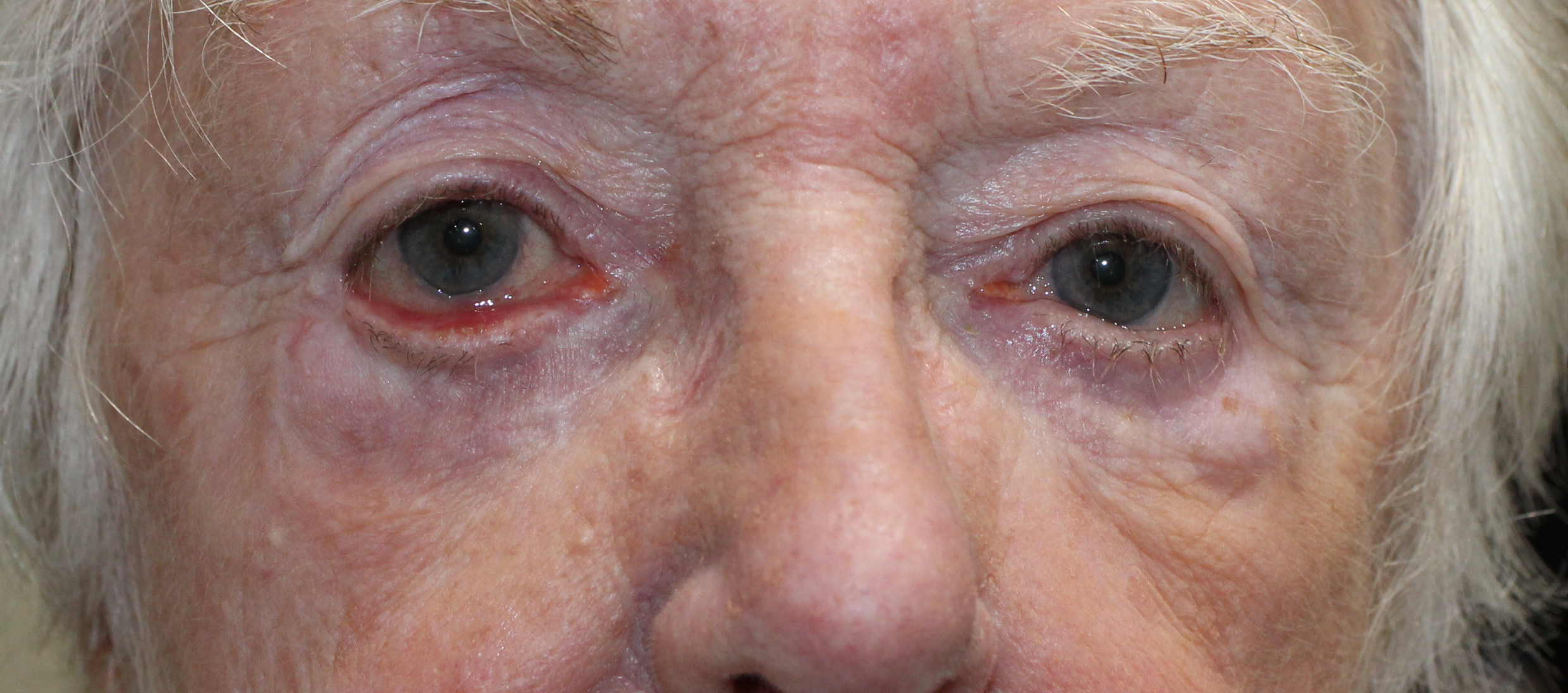
Understanding Eyelid Dermachalasis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options.
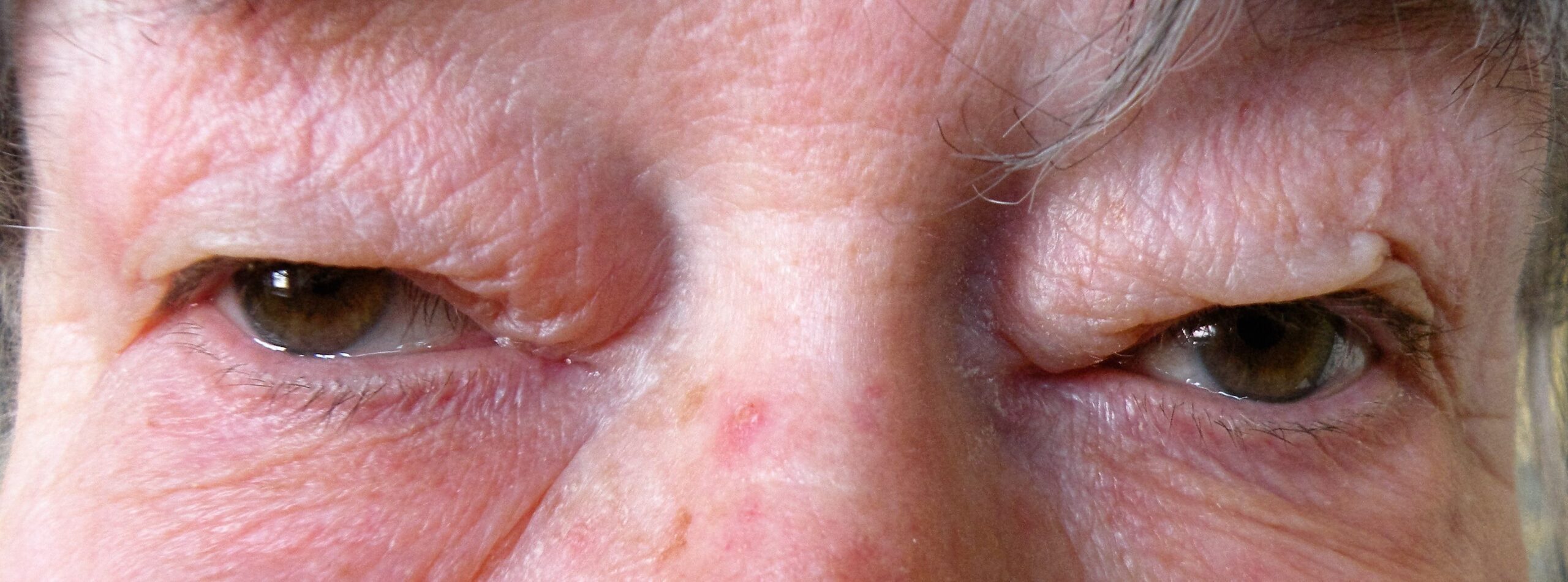
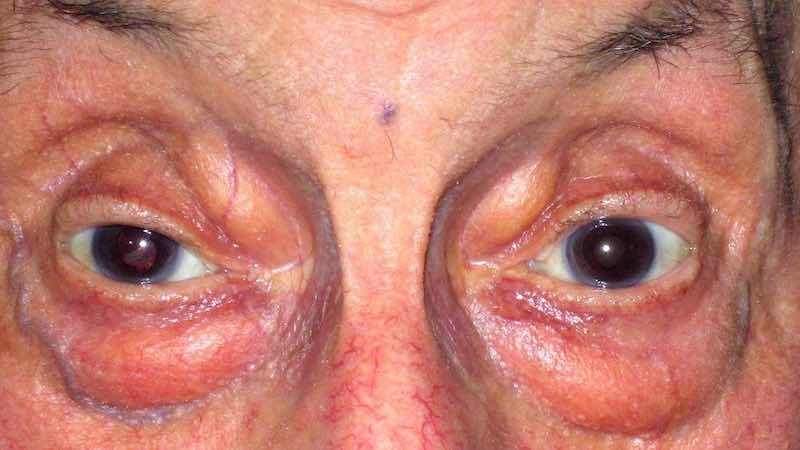
Eyelid dermachalasis is a condition characterised by the sagging or excess skin of the upper or lower eyelids. This cosmetic issue is often associated with ageing, but it can also occur due to genetic factors, environmental influences, or specific medical conditions. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for eyelid dermachalasis can help individuals make informed decisions about their eye health and appearance.
Causes of Eyelid Dermachalasis
The primary cause of eyelid dermachalasis is the natural ageing process. As people age, the skin loses collagen and elastin, two essential proteins that provide skin with firmness and elasticity. This loss leads to the development of loose, sagging skin, particularly around the eyes, where the skin is already thin and delicate.
Other contributing factors include:
- Genetics: Family history can play a significant role. Individuals with relatives who have experienced dermachalasis are more likely to develop the condition themselves.
- Sun Exposure: Prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays can accelerate skin ageing, leading to a breakdown of collagen and elastin. This environmental factor can contribute to the development of loose skin around the eyes.
- Lifestyle Factors: Smoking, poor nutrition, and inadequate hydration can impact skin health and promote premature ageing, increasing the risk of dermachalasis.
- Medical Conditions: Certain medical issues, such as thyroid disorders, can lead to changes in skin texture and contribute to eyelid sagging.
Symptoms of Eyelid Dermachalasis
The most noticeable symptom of eyelid dermachalasis is the appearance of excess skin on the eyelids, which can lead to several aesthetic and functional problems:
- Sagging Skin: This can create a tired or aged appearance, as the eyelids may droop or appear puffy.
- Impaired Vision: In more severe cases, excess skin can obstruct peripheral vision, making it difficult to see clearly.
- Discomfort: Some individuals may experience irritation or discomfort due to the sagging skin rubbing against the eyelashes or causing sensitivity.
- Cosmetic Concerns: Many people seek treatment for dermachalasis due to its impact on their appearance, which can affect self-esteem and confidence.
Treatment Options
Treatment for eyelid dermachalasis varies based on the severity of the condition and the patient’s preferences. Options include:
- Non-Surgical Treatments: For mild cases, non-invasive treatments such as laser therapy, radiofrequency treatments, or chemical peels may help tighten the skin and improve its appearance. These options can stimulate collagen production and enhance skin elasticity but may not provide the dramatic results that surgical options offer.
- Blepharoplasty: The most common surgical treatment for eyelid dermachalasis is blepharoplasty, also known as eyelid surgery. This procedure involves the removal of excess skin and sometimes fat from the eyelids to restore a more youthful and refreshed appearance. Blepharoplasty can address both upper and lower eyelids.
- Lifestyle Modifications: While they may not eliminate dermachalasis, lifestyle changes such as wearing sunscreen, maintaining a healthy diet, staying hydrated, and avoiding smoking can help improve overall skin health and delay further ageing.
Conclusion
Eyelid dermachalasis is a common condition that can affect both appearance and vision. Understanding its causes and symptoms is essential for those experiencing this issue. While non-surgical treatments can offer some improvement, surgical options like blepharoplasty remain the most effective solution for significant cases. Individuals concerned about eyelid dermachalasis should consult us to explore the best treatment options tailored to their needs. With appropriate care, it is possible to achieve a more youthful and vibrant appearance.
